Have you noticed that more and more foundations are moving to "no unsolicited proposals" policies? You research a foundation that looks like a perfect fit for your organization, only to discover that it only accepts proposals by invitation.
It's not your imagination. The door to foundation funding has been closing slowly for years—and the data proves it.
In 2011, 60% of foundations didn't accept unsolicited proposals (Smith, 2011). By 2015, that number jumped to 72% (Eisenberg, 2015). According to Candid's most recent research analyzing over 112,000 private foundations, 71% now only fund "pre-selected charitable organizations" (Candid, 2024).
That means only 29% of foundations will even look at your proposal unless they've invited you to apply. But 2026 might be the year that the remaining door slams shut for good—and sloppy AI is the reason.
Foundations are already overwhelmed. With AI making it easier than ever to churn out generic grant proposals, program officers are drowning in poorly-written applications using the outdated spray-and-pray method. According to Candid's 2024 Foundation Giving Forecast Survey, 23% of foundations already won't accept AI-generated proposals, and 67% are still figuring out their policies (Mika, 2024). This was an anonymous survey, which allowed foundations to be more candid about their concerns—most haven't made public statements about AI policies yet, so this data reveals what's happening behind the scenes.
Translation: Those foundations that still accept unsolicited proposals are one bad grant cycle away from going invitation-only permanently.
And if you're still using spray-and-pray—sending generic proposals to every foundation you find—you're not just wasting your time. You're actively contributing to the problem that's closing doors for everyone.
The Spray-And-Pray Era Is Over
You know the drill: Research 50 foundations, send essentially the same proposal to all of them, hope for the best.
Here's the thing—it never really worked. But now? It's actively harmful.
Here's what's happening behind the scenes:
Foundation program officers are receiving more proposals than ever. Many are clearly mass-produced. Some are obviously AI-generated by people who don't understand grant writing fundamentals. The quality is declining while the volume is increasing.
The foundation's response? Close the door. No more unsolicited proposals. Invitation only. By the time you realize that perfect-fit foundation has gone invitation-only, you've already lost your chance.
The Real Problem Isn't AI—It's Inexperience
Let me be clear: The problem isn't AI itself. The problem is using AI to write grant applications when you don't have the experience to know whether AI is doing it right.
Think about it: If you don't understand what makes a compelling needs statement, how will you know if the AI-generated needs statement is compelling? If you can't identify a good organizational fit for grant funding, how will you evaluate whether AI matched you with the right funders?
Learn grant writing first. Master strategic thinking, understand what makes proposals fundable, and develop your judgment about fit and quality. Then use AI to make your work more efficient. AI can help you write faster, generate first drafts, and organize information—but only if you have the grant writing expertise to direct it and evaluate its output.
How Foundations Spot Sloppy Ai Proposals (Hint: Not Through Detectors)
You might be wondering: Are foundations using AI detection software to screen out AI-generated proposals? The short answer is no, and they don't need to. AI detectors don't work reliably, producing high rates of false positives and false negatives. They flag human-written content as AI-generated and miss obvious AI content. Even the companies that make these tools acknowledge their limitations. But here's the thing: foundations don't need detection software to spot poorly-written AI proposals. The problems with sloppy AI grant writing are obvious to any experienced grant reviewer, not because they "sound like AI" but because they lack the substance, specificity, and strategic thinking that characterize strong proposals.
Bad AI proposals reveal themselves through lack of substance:
• Flowery statements without evidence: "Our innovative, transformative program creates lasting change in the community," → but no data on how many people served, what outcomes were achieved, or what "transformative" actually means
• Generic descriptions that could apply to anyone: Any youth development organization could claim the same things, any food bank could use the same language
• Buzzword soup without specifics: Talking about "strategic partnerships" and "collaborative impact" without naming a single partner or describing what the collaboration actually looks like
• Perfect grammar, disconnected logic: Beautiful sentences that don't actually connect to each other or build a coherent argument
• Misunderstanding the funder's actual priorities: The AI matched keywords, but the proposal shows the applicant doesn't really understand what the foundation cares about
• Overpromising without realistic plans: Grand claims about impact that don't match the organization's budget, staffing, or track record
The tell isn't that it "sounds like AI"—it's that it lacks the authentic details, specific evidence, and strategic understanding that only comes from someone who truly knows both the organization and grant writing.
A proposal written by an experienced grant writer using AI thoughtfully? It still has those specifics, that evidence, that strategic fit assessment. Because the human knows what details matter and how to direct the AI to strengthen (not replace) their expertise.
The Strategic Alternative: Quality Over Quantity
So if spray-and-pray is dead, what's the alternative?
Strategic grant writing. And it starts with one critical skill: knowing when NOT to apply.
This might sound counterintuitive. You need funding, so shouldn't you cast the widest net possible? Actually, no. That approach wastes your limited time and contributes to the problem that's shutting down access for everyone. Instead, you need to become ruthlessly strategic about where you invest your grant prospecting effort.
Focus on Low-Hanging Fruit First
Low-hanging fruit doesn't mean "easy grants that everyone wins." It means perfect fit funders—foundations where the alignment between your work and their priorities is so clear that your proposal practically writes itself.
What does a perfect fit look like? Start with mission alignment. The foundation funds exactly the kind of work you do—not tangentially related, not sort of similar, but directly aligned. If you run an environmental education program for youth, you're looking for foundations that specifically fund environmental education for youth, not just "youth programs" or "environmental causes" broadly.
Geographic alignment matters too. You need to be squarely in their funding area. If a foundation focuses on three specific counties and you're in one of them, that's a good fit. If they fund the entire Pacific Northwest and you're in Seattle, you're competing with hundreds of other organizations. Be honest about whether you're in the sweet spot or on the periphery.
Grant size alignment is equally important. If you need $50,000 and a foundation typically gives $5,000 grants, you're not a fit—no matter how perfect the mission match. Look at their grantmaking history using tools like Candid's Foundation Directory. What's their typical range? Do they ever make grants at your level? Don't waste time trying to convince a small family foundation to make their largest grant ever to your organization.
Finally, look at their history of funding organizations like yours. When you review their past grantees, can you genuinely say "of course—we should be on that list too"? That's what I call the "of course" factor.
Getting to "Of Course"
The "of course" factor is that moment when a grant reviewer reads your proposal and thinks "of course that makes sense" and "of course we want to fund that." You've achieved a strategic fit so clear that funding feels obvious.
Getting to "of course" requires deep research. You need to understand what the foundation values, not just what they say they fund. Read their annual reports. Study the organizations they support. Look for patterns in who gets funding and why. What do their grantees have in common? What kinds of projects do they prioritize—pilot programs or proven models? Direct service or capacity building? Local grassroots organizations or regional powerhouses?
When you can see yourself clearly in that pattern of funding, you've found low-hanging fruit. These are the opportunities where you should spend 80% of your grant writing time. Perfect the proposal. Build the relationship. Demonstrate the fit. These are your highest probability opportunities, and they deserve your best effort.
Long-Shots Can Work—But Only With Strategy
I'm not saying you should never pursue a foundation that's a less obvious fit. Long shots aren't impossible. But they require a fundamentally different approach than spray-and-pray.
A legitimate long-shot means you've identified a genuine strategic connection that might not be obvious at first glance, and you're willing to invest significant time proving it. Maybe the foundation primarily funds healthcare, but they've shown interest in addressing social determinants of health, and your housing stability program directly impacts health outcomes. That's a strategic long-shot—there's a real connection, but you need to make the case.
What makes a long shot worth pursuing? You need a clear, compelling angle for how your work fits their mission, even if your project doesn't look exactly like what they typically fund. You need to be willing to build the relationship first—attending their events, engaging with their published research, and making personal connections with staff or board members. And you need to go all-in on the application itself. Don't submit a recycled proposal with minor tweaks and hope for the best. If you're going after a long shot, treat it like the long shot it is: invest the time to craft a proposal that explicitly makes the strategic connection clear.
Don't apply to long-shots as a numbers game, hoping that if you submit to enough "maybes," a few will pay off. That's just spray-and-pray with better targeting. Apply to long-shots only when you've done the strategic thinking, and you're prepared to do the work.
The Middle Ground: Be Selective
Then there are mid-range opportunities—foundations where you have good but not perfect alignment. Maybe your geographic area overlaps with theirs, but it isn't their primary focus. Maybe your mission connects to theirs tangentially. Maybe they fund your issue area, but usually support larger organizations.
These require judgment. Some are worth pursuing. Many aren't. The question to ask yourself: Can you genuinely demonstrate fit, or are you just checking boxes? If you're writing a proposal, thinking "well, we kind of fit because..." stop. That's not strategic. That's spray-and-pray disguised as research.
Be selective. Choose the opportunities where you can make a clear, honest case for why you belong in their funding portfolio. Skip the rest.
The Hidden Costs Of Spray-And-Pray
Beyond wasting your time, the spray-and-pray approach to grant writing has real consequences:
Reputational damage: Foundations talk to each other. Submit poorly-matched proposals consistently, and you develop a reputation as someone who doesn't do their homework. In the tight-knit world of philanthropy, that reputation follows you.
Opportunity cost: Every hour spent on a bad-fit proposal is an hour not spent on a good-fit opportunity. If you can write 5 excellent, strategic proposals or 20 mediocre, generic ones, which will raise more money? The data from the Grant Professionals Association shows that grant professionals are already being more selective—writing a median of 19-20 proposals per year, not 50 or 100 (Grant Professionals Association, 2023). Quality matters more than quantity.
Contributing to the problem: Every generic, poorly-matched proposal that lands in a program officer's inbox makes them more likely to close the door to unsolicited applications entirely. You're not just hurting your own chances—you're making it harder for every nonprofit organization.
Diminishing access for everyone: When foundations go invitation-only because they're overwhelmed with poor applications, you've just made it harder for every nonprofit—including yours—to access foundation funding in the future. This particularly impacts smaller organizations and those serving marginalized communities who have fewer insider connections.
What This Means For 2026
The data is clear: Foundations have been moving toward invitation-only policies for over a decade. AI hasn't created this trend—but sloppy use of AI is accelerating it.
In 2026, the strategic grant writers will thrive.
They'll focus on fit, build relationships, and demonstrate an authentic understanding of both their organizations and their funders. They'll use AI as a tool to enhance their expertise, not replace it. They'll invest in professional grant writing training to develop the judgment needed to evaluate quality.
The spray-and-pray crowd will find fewer and fewer doors open.
Which side of that divide do you want to be on?
What You Can Do Right Now
1. Audit your current prospect list. Remove any foundation where you can't clearly articulate why you're a strong fit. If you're using a prospect tracking spreadsheet, add a "fit score" column and be honest about each opportunity.
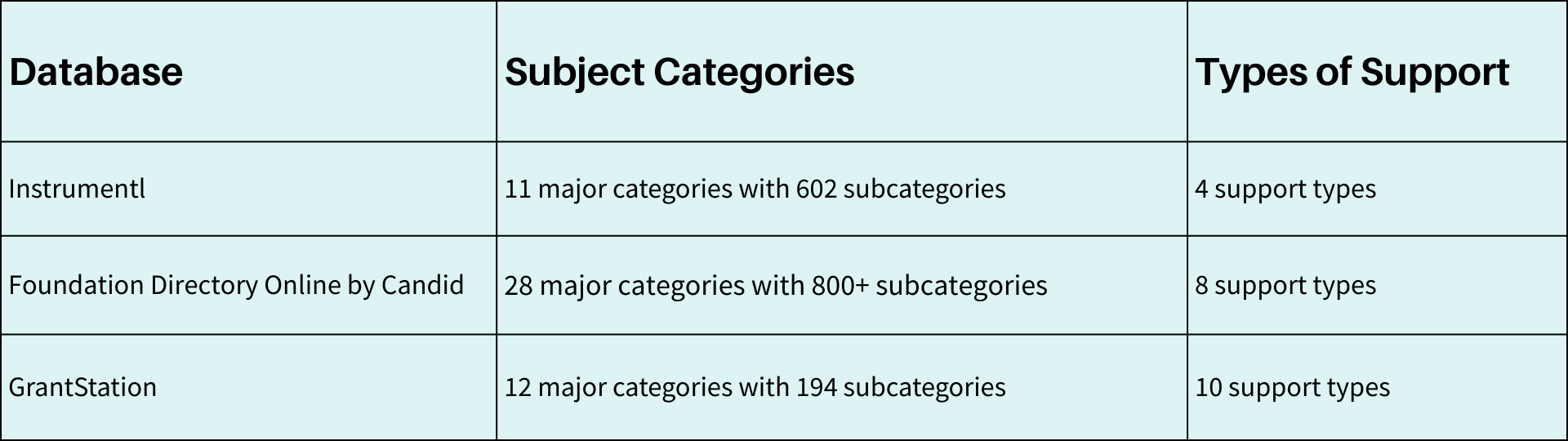
2. Research thoroughly before applying. Look at 3-5 years of past grantees using resources like Instrumentl, Candid, or foundation 990-PF forms. Can you genuinely say, "Of course, we belong on this list"? If not, move on.
3. Invest in learning. If you're using AI to write proposals, make sure you have the grant writing expertise to evaluate and improve what AI produces. Consider professional certification in grant writing to build that foundation.
4. Build relationships. Don't let your first contact with a foundation be a proposal. Attend their events, engage with their content, and make connections. Relationship-based fundraising still works—even in an AI era.
5. Track your success rates by fit level. Are your "perfect fit" applications succeeding? If not, the problem isn't fit—it's proposal quality. Get help with grant writing training or hire an experienced consultant.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How can I tell if a foundation is a good fit for my organization?
A: Look at four key alignment factors: mission (do they fund exactly what you do?), geography (are you squarely in their funding area?), grant size (do they give grants at your level?), and grantee history (when you look at who they fund, do you belong on that list?). If you can't clearly articulate why you fit in all four areas, it's probably not worth applying.
Q: Should I never use AI for grant writing?
A: AI can be a powerful tool for experienced grant writers—it can help generate first drafts, organize information, and improve efficiency. The problem is using AI when you don't have the expertise to evaluate whether its output is good. Learn grant writing fundamentals first, then use AI to enhance your work.
Q: What if all the foundations in my area don't accept unsolicited proposals?
A: This is increasingly common. Your strategy shifts from "submit proposals" to "build relationships." Research foundations that align with your work, identify connections (board members, staff, funded organizations you know), and start relationship-building. Attend their events, engage with their content, and ask for informational conversations. The goal is to get invited to apply.
Q: How many grant proposals should I be submitting per year?
A: According to Grant Professionals Association data, grant professionals write a median of 19-20 proposals per year. Quality matters far more than quantity. It's better to submit 10 highly strategic, well-researched proposals than 50 generic ones.
Q: How do I know if my proposal is too generic?
A: Ask yourself: Could another organization in your field submit this exact same proposal by just changing the name? If yes, it's too generic. Strong proposals include specific data about your organization, concrete examples of your work, and clear evidence of why you're the right organization for this funder at this time.
Q: What's the difference between a strategic long-shot and spray-and-pray?
A: A strategic long-shot means you've identified a genuine connection between your work and the funder's priorities (even if it's not obvious), and you're willing to invest significant time building the relationship and crafting a targeted proposal. Spray-and-pray means sending essentially the same proposal to many funders, hoping something sticks, without strategic thinking about fit.
The Bottom Line
The landscape of foundation fundraising is changing. The doors are closing—not because foundations don't want to fund good work, but because they're overwhelmed with poor applications from organizations that haven't done the strategic thinking.
Strategic grant writing isn't just about writing better proposals. It's about making better decisions about where to invest your limited time. It's about knowing when to walk away from a poor-fit opportunity. It's about building relationships and demonstrating a genuine understanding of what funders care about.
If you're serious about foundation funding in 2026 and beyond, it's time to stop throwing applications at every foundation you find and start being strategic about fit.
The foundations that remain open to unsolicited proposals are looking for thoughtful, strategic applications from people who've done their homework.
Give them what they're looking for—and stop contributing to the problem that's closing doors for everyone.
Now I want to hear from you: Have you noticed foundations in your area closing to unsolicited proposals? Are you seeing AI-generated proposals flood your field? And honestly, where do you fall on the spray-and-pray to strategic spectrum? Share your experience in the comments.
References
Candid. (2024). How often do foundations accept unsolicited requests for funds? https://candid.org/blogs/do-foundations-accept-unsolicited-requests-for-funds-from-nonprofits/
Eisenberg, P. (2015, October 20). Let's require all big foundations to let more nonprofits apply for grants. Chronicle of Philanthropy.
Grant Professionals Association. (2023). 2023 GPA compensation and benefits survey. https://grantprofessionals.org/page/salarysurvey
Mika, G. (2024, December 5). Where do foundations stand on AI-generated grant proposals? Candid Insights. https://blog.candid.org/post/funders-insights-on-ai-generated-grant-application-proposals/
Smith, B. K. (2011). [Foundation Center research on unsolicited proposals]. Referenced in Nonprofit Quarterly. (2017, February 24). Scaling the wall: Getting your grant proposal heard. https://nonprofitquarterly.org/scaling-the-wall-getting-your-grant-proposal-heard/